ACTION C.5 – Establishment of optimization of an integrated, population-level surveillance of brown bear conservation status
Understanding of population parameters (population size, sex ratio, fecundity/mortality, spatial extent) and their temporal dynamics is one of conservation and management foundations for any animal population. The goal of this action is to start a comprehensive, optimized scheme for monitoring of the Alpine-Dinaric bear population that will cover its entire range within the participating countries.
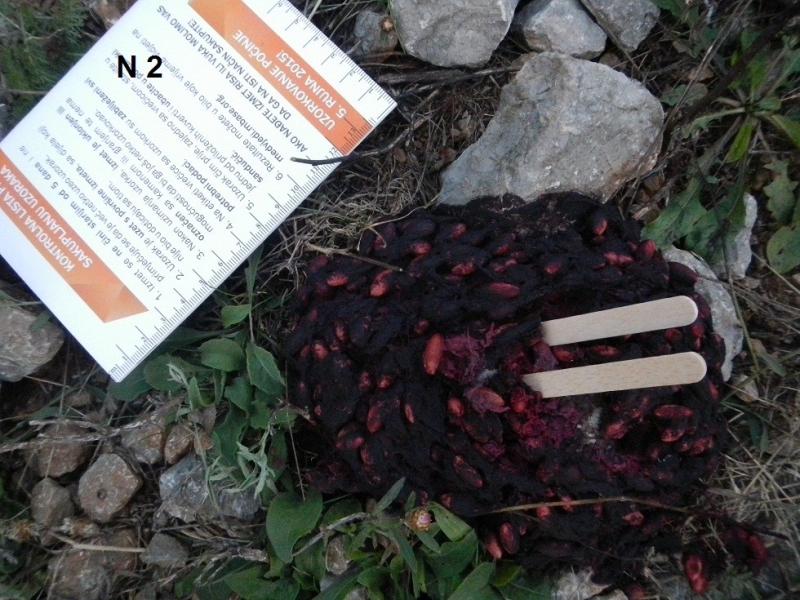
Genetic sampling of brown bears is scheduled in all participating countries. Sampling will be done through non invasive methods in the core range of brown bear in Slovenia and Croatia and will involve hunters, foresters and other interested volunteers, combined with data collected in Action D.1. Opportunistic, year-round sampling will be done in the recovery zone in north-western part of the study area (western Slovenia, Italy and Austria).
Tissue samples and tooth cementum samples are routinely collected from detected bear mortality. We will used them to infer population size estimates, age structure and effective population size. Genetically tagged animals appearing in the cull will help us understand dispersal and population dilution through reproduction.
Counting bears on permanent counting sites will give us an estimate of minimum number of bears, number of cubs per female, relative dynamics of population size, reproduction and population range. Counting will be done by hunters three times a year in specific weather conditions.
There is already a wealth of information on lifetime reproductive output, primiparity and sex or age specific reproductive success. By augmenting these data from permanent counting sites, parentage and relatedness analysis, genetic data and inspection of reproductive organs of deceased bears we will be able to better understand age and sex specific reproductive outputs.
Veterinarians will inspect cadavers of deceased and live caught bears for infectious diseases and health status.
We will analyze currently implemented systems to handle damages done by bears in all participating countries for possible insufficiencies. To improve exchange of data and share experiences in population management and monitoring, we will compile a report of possible suggestions to harmonize data collection using experiences gained through collaboration.
By comparing all methods of estimating population sizes against currently most reliable estimates from genetic sampling, we will suggest the most cost-effective monitoring scheme which can be used when more expensive but also more precise methods are not available.
Latest C.5 actions:
Press release in Croatia: Counting bears and collecting of samples has started
On the occasion of the implementation of the action of counting bears in Croatia and Slovenia by using genetic sampling [...]
Media release on progress of sampling bear scats
An important aspect in managing bears is to know the population status, especially regarding its size. One activity in LIFE DINALP [...]
Workshops for monitoring (genetic sampling) of brown bear and wolf in Slovenia
On August 17 and August 18, workshops for monitoring of brown bear (Life DinAlp Bear) and wolf (Slovenian national monitoring) [...]
T-shirt design contest is over
Deadline for sending in your t-shirt designs is over. Everyone who participated will receive a thank you gift (a T-shirt [...]
Preparation for autumn genetic sampling are in full swing
Preparations for autumn non-invasive sampling of bears in Slovenia is in full swing. In the past two weeks we delivered [...]
Distribution of sampling kits for genetic counting of brown bears (Action C. 5) started in Croatia
Distribution of sampling kits for collecting brown bear fecal samples for genetic analyses in Croatia started yesterday (9.7.2015) with three [...]